Make a Project Schedule that is easy to Understand
Schedules can be an amazing way to stay on track. Project schedules map the project tasks and milestones for you, so that you always know what comes next. Start by making a project schedule that is easy to understand. The project schedule should contain all the important information you need to know about your project.
When first considering developing a project schedule, it is important to structure it in such a way that it is simple to understand. However, a simple schedule should also detail your requirements to give a good overall impression of the work. Developing a good project schedule is about striking the right balance of information to ensure the work is carried out as planned.
The Project Management Institute (PMI) has a structured and detailed approach to building a project schedule. This blog discusses a set of best practices to execute an efficient schedule.
How to Make a Project Work Breakdown Structure
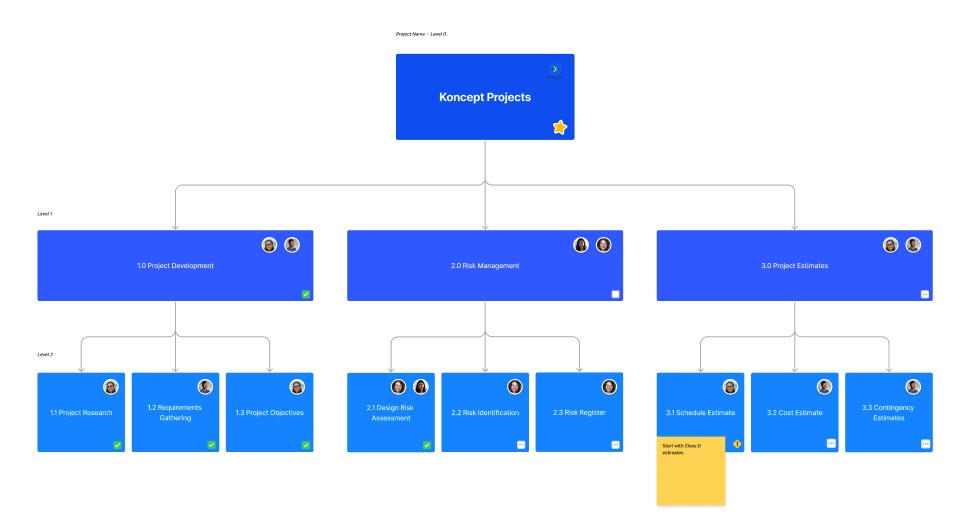
To develop the work breakdown structure, begin by asking “what” needs to be done? It’s important to divide the work in the manageable buckets. This first step will help ensure the project is simple and easy to understand at a quick glance.
The WBS should not be developed in isolation, consider engaging with the wider team. The project schedule could be jeopardized if a critical work package element is overlooked during this process. There are two main formats that you can use when beginning the WBS. You can write an outline or develop a visual chart.
I appreciate visual learning so; the use of charts is helpful because it gives me a sense of size and scale. Developing a WBS can be simple and are often aided by technology. However, you can also start by using a whiteboard or sticky notes to determine the different levels of details.
Easy to Use Work Breakdown Structure Software
Figma is a collaborative interfaced design tool. Figma connects everyone in the design process so teams can deliver better products, faster. The WBS above was developed in Figma.
Lucidchart offers a visual workspace that combines diagramming, data visualization, and collaboration to accelerate understanding and drive innovation.
A full WBS can be broken down into many levels depending upon the organizational requirements. As the project manager you can make the WBS as detailed as you need. The 8/80 rule is a way not to go too deep into any one part of your project while ensuring you stay on track.
Use the 8/80 Project Scheduling Rule

Do not break a task down below 8 hours. Conversely, if a task is longer than 80 hours, it should be broken down into lower-level work packages.
How to Understand Schedule Relationships
Determining the logic is where all the hard work comes together or falls apart. Care must be taken to ensure the logic is reasonable and accurate. Every activity except the first and last one will have a predecessor and successor.
A common mistake is developing logic for the Work Package. When this happens the logic overrides and there is confusion between the activities and summary work package. The confusion can change and modify the critical path.
A false representation of the critical path may result in prioritizing less important schedule activities and incorrect resource allocation.
Define Finish-to-Start Schedule Relationship (FS)

The most popular and used logic is the finish-to-start relationship. The use of this type of logic leads you to the conclusion that the following activity cannot commence until the prior action has been completed.
A good example of this is that the concrete foundation needs to be poured before you can start framing.
Define Finish-to-Finish Schedule Relationship (FF)

The Finish-to-Finish (FF) relationship prevents the successor activity from advancing until the predecessor activity is finished. When these two things can be done largely at the same time, they are usually seen as being concurrent.
For example, a project coordinator might work on the presentation in parts before handing it over to the project manger who then edits it and adds some finishing touches. The FF logic is normally accompanied with lead(s) or lag.
Define Start to Start Schedule Relationship (SS)

A Start-to-Start relationship and is used to represent the idea that this chain of events needs to be considered. This applies if the two activities can be performed in parallel. However, some work must begin before the other activity can start. The SS logic is normally accompanied by lead(s) or lag.
Define Start-to Finish Schedule Relationship (SF)

The Start-to-Finish relationship isn’t used that often. SF means that the successor activity can’t start until the predecessor one ends. When using SF, it might cause issues with the critical path generation. This would mean you might have to rethink your logic.
How to Determine Project Schedule Resources
For many, the process of selecting resources for a project is daunting. But it can be helpful to have experts from the team to lead you in the right direction. They can offer guidance on what needs to be considered when designing a project and help you select which tools and materials will be most useful for your project.
Here are a few things you might need before getting started: Is there the right level of expertise for this activity? What are your human resource needs? What tools and materials can ensure you attain the goal?
In all instances you will need to define the amount of work required for each resource. Depending on what scheduling tool you’re using, the resources allocation will be calculated as (100%) for the duration of the activity based off one person. You will need to adjust this based upon the number of resources allocated to the task.
How to Define Schedule Activity Durations

At this point, you should have all the information you need to determine how many resources are required to complete the project. However, defining the duration of an activity can be tricky, so you need to build in assumptions.
For instance, allocating a resource for 100% productivity every day on the entire project. This is an easy trap to fall into. However, it would be best to assume that the resource would be somewhere between 85%-95% productive throughout the day. So, you need to set realistic expectations for utilization. Doing so will help improve your overall schedule accuracy.
When defining the schedule, some additional questions to consider are: Will the resources be allocated to the project 100% of the time? If not, what percentage of allocation do you assume? Will the project undergo a formal tender? Will the lowest bid be selected, and how will this affect our resourcing capacity?
How to Analyze the Project Schedule
Analyzing the Project Schedule

Your work has paid off and your schedule is complete, congrats! The last step us to determine if everything makes sense and the plan will work. I like to focus on the critical path to ensure the logic is correct and there are no disconnects. This is also a good time for the extended team to review and gain alignment on the critical path and ensure everyone understands the importance.
When considering tasks on the critical path this is good time to review the risk register and focus on adjusting the schedule for risk. The team will want to focus their efforts on areas that may affect the critical path. If a risk was to become realized would the critical path change?
Significant benefits can be discovered by integrating risk into the schedule. This is an area that is often ignored by Contractors and Owners. The process of identifying problems and other potential issues, brainstorming possible solutions and calculating time contingencies will greatly improve results.
Are milestones realistic and connected to financial goals and targets. Milestones often reveal logical relationships meaning, milestone 2 cannot be completed before milestone 1. Milestones are linked to contractual requirements. That way we can be sure to include them in our schedule.
Recommended Project Management Scheduling Software
Now that your WBS is complete, it’s time to start coordinating your schedule and importing the tasks into your project management system. The following scheduling software can help with your next project:
Oracle – Primavera P6 Enterprise Project Portfolio Management
Manage projects of any size with Primavera P6 EPPM. Robust, and easy-to-use, Primavera P6 EPPM is the solution for globally prioritizing, planning, managing, and executing projects, programs, and portfolios.
Microsoft Project
Stay organized, focused, and in charge. Tackle anything from small projects to large initiatives. You may or may not be a project manager, but now you can be the boss of any project with a powerful, easy-to-use app.
Deltek OpenPlan
A robust schedule management solution that offers the power and flexibility to help complete medium-to-large and/or multiple projects on time and on budget. A key product in our PPM suite, Open Plan includes advanced project scheduling features like multi-project analysis, critical path planning, resource management and risk analysis to help improve plan and schedule quality. Advanced features help identify quality issues and improve compliance with industry and company standards and best practices.
Wrike
Wrike’s customizable features include Gantt charts, request forms, dashboards, cross-tagging, time tracking, and proofing. Integrate with 400+ apps from the likes of Microsoft, Google, and Salesforce. Automate repetitive tasks and achieve 50% faster planning. Work from anywhere with 100% access to your files via our mobile and desktop apps.
